Monitoring Network Hops to Peers
5 minute read
This feature collects traceroute-like data from all its connected peers and stores the results in the Trustgrid cloud for historical review.
How it Works
- The node will send out TCP SYN packets to each peer’s public IP and port (if a gateway) with incrementing Time To Live (TTL) values every 20 seconds.
- As the packets pass through each router (or hop) along the way the TTL is decreased by one.
- Any time a router receives a packet with a TTL value of 1 it will drop the packet and can reply with an ICMP packet saying “Time to Live has been exceeded”
- The node uses these ICMP packets to calculate the latency to each hop.
Known Limitations
There are several known limitations to gathering this data:
- Routers on the internet are not required to respond with ICMP. This will lead to gaps in the Hop numbers.
- Those that do respond sometimes deprioritize their response which leads to misleading latency numbers.
- If you see a hop with high values, but the values for higher hop numbers are normal this is not likely the cause of problems
- If a hop has high values and all subsequent hops have higher values this is likely the source of the latency/loss
- Firewall rules have to allow the packets and the responses.
- By utilizing the same TCP port as the gateway, all data collected from edge nodes should be allowed out.
- Some firewalls/routers have trouble correlating the TCP request with the ICMP response which leads to no data
- Gathering this data requires compute resources on the node and the gateway. Trustgrid recommends only enabling on edge nodes that have frequent latency or packet loss issues as a troubleshooting tool.
Enabling Network Hop Monitoring
There are two ways to enable hop monitoring:
Enable on a Specific Edge Node
This method will configure the node in question to attempt hop monitoring to all connected gateway peers.
- Navigate to the node you want to enable
- In the left side navigation bar select Gateway under the System section. Then click the Client panel.

Navigating to the client panel - Set the Monitor Hops to Gateway Servers to Always.
- Click Save
Enable on a Gateway Node
This method will tell all connected peers running the correct version of the node software to attempt hop monitoring to this specific gateway.
- Navigate to the gateway node you want to enable.
- In the left side navigation bar select Gateway under the System section. Then click the Server panel.

Navigating to the server panel - Set Request Clients Monitor Hops to Enabled.
- Click Save
Special Considerations
Azure Nodes
If you enable this on an edge node running on an Azure VM, the default security group rules will prevent responses from intermediate hops on the path. You will still get data from the final hop, which is the target gateway.
You will need to add an inbound rule to the node’s public interface network security group.
The rule needs the settings shown below:

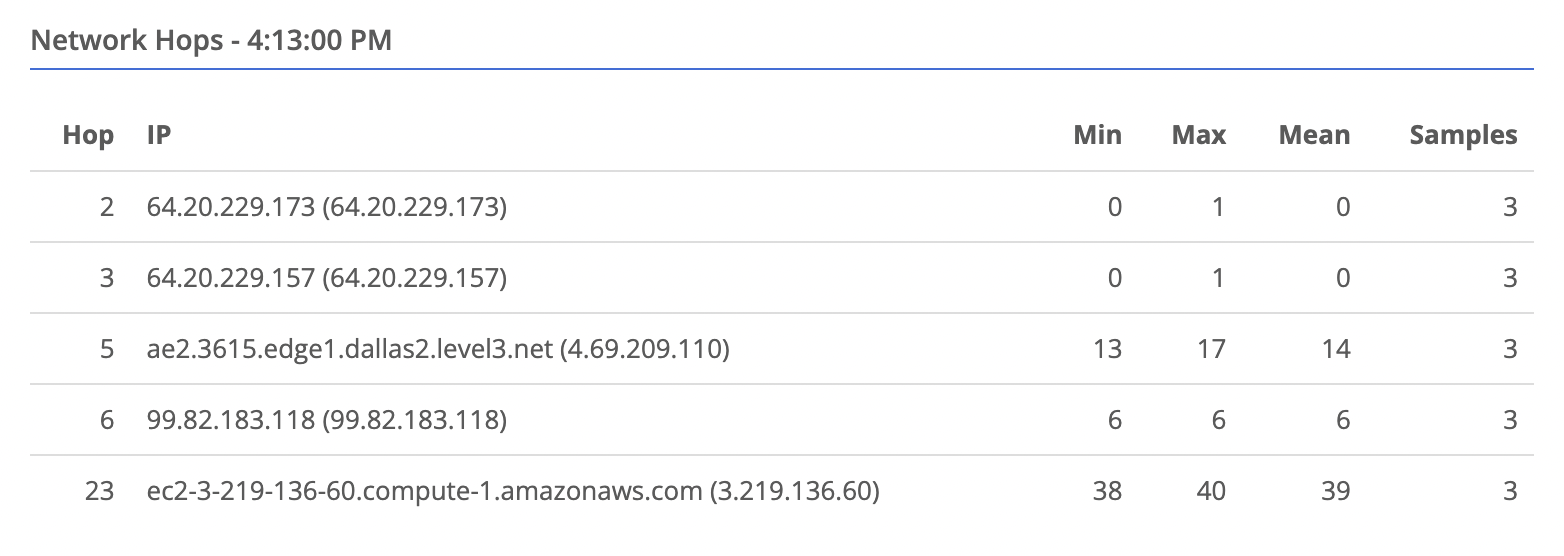
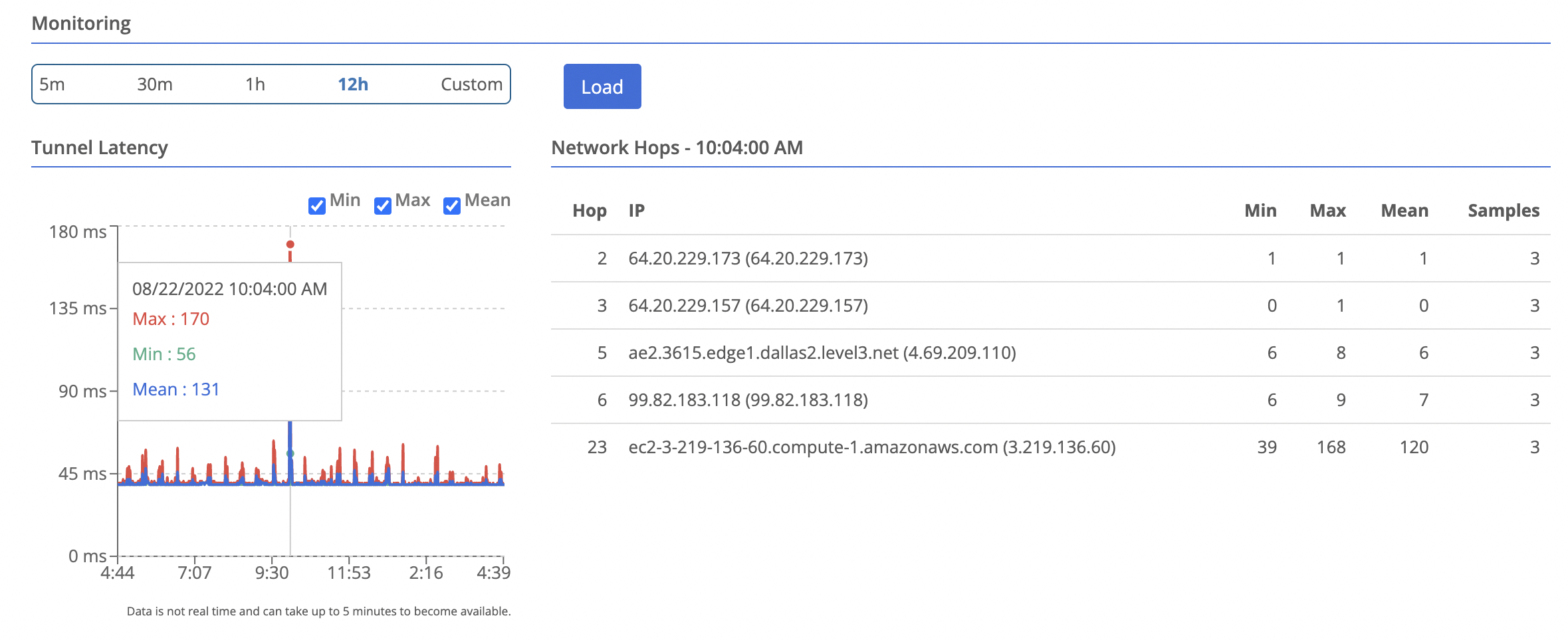
Viewing Network Hop Data
- Navigate to the node you want to view
- Select Data Plane on the left
- Select the peer you wish to view data for. You will see a table of hops appear in the bottom right.
- You can select a time point on the latency chart, and the hops table will update to show the data for that time point.
Advanced Client Settings
In the Client panel there are additional settings that can be changed to alter how hop monitoring is performed. These settings include options for adjusting the monitoring interval, payload size, and if the node should send reset packets for the TCP connections it attempts.
Lowering the Interval
The default setting of 20 seconds provides 3 data points per minute. Lowering the interval would provide additional granularity in the monitoring data, increasing the chance packet loss could be detected. However, could cause network devices in the path to view the increased traffic as a potential threat, leading to possible rate limiting or other security measures being applied.
Increasing the Payload Size
A larger payload size can highlight lower than expected maximum transmission unit (MTU) values along the path. This can be useful for identifying potential bottlenecks or misconfigurations in the network. However, like an increased interval, it could cause network devices in the path to view the increased traffic as a potential threat, leading to possible rate limiting or other security measures being applied.
Recommendation
Changing both these settings can be helpful if a node is seeing high latency to one or more peer devices, and the risk of the traffic being misidentified as a potential threat. It is recommended to change these settings on nodes actively experiencing issues and monitoring the impact it has on the node, the peer and the overall connection performance.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.